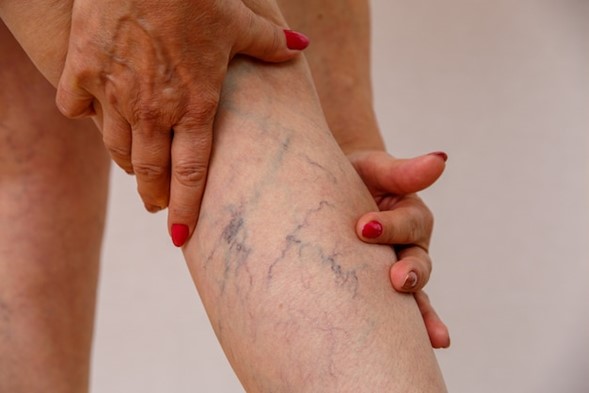
Varicose veins are a common yet often misunderstood condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Characterized by swollen, twisted veins visible just beneath the skin, they can cause discomfort and sometimes lead to more serious health concerns. But what exactly causes varicose veins, and how can they be managed or treated? Let’s dive deeper.
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins occur when veins become enlarged and overfilled with blood. They most commonly appear in the legs and feet due to the increased pressure in these areas from standing and walking. While often seen as a cosmetic concern, varicose veins can also cause physical symptoms such as pain, swelling, and heaviness in the legs.
Causes of Varicose Veins
The primary cause of varicose veins is faulty valves within the veins. Normally, these valves ensure blood flows toward the heart. When they malfunction, blood can pool in the veins, causing them to stretch and become varicose. Factors that increase the risk of developing varicose veins include:
- Age: The risk increases with age as vein elasticity diminishes.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, and the use of hormonal birth control.
- Family History: Genetics can play a significant role.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Occupations requiring long periods in these positions can increase risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight adds pressure on veins.
- Pregnancy: Increased blood volume and pressure during pregnancy can lead to varicose veins.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Not all varicose veins are symptomatic, but when they are, symptoms can include:
- Swollen, bulging veins that are visible under the skin
- A heavy or achy feeling in the legs
- Burning, throbbing, or muscle cramping in the lower legs
- Swelling in the ankles and feet
- Itching around the affected veins
- Skin discoloration or ulcers near the ankles (in severe cases)
Treatment Options
Treatment for varicose veins ranges from lifestyle changes to medical procedures, depending on the severity of the condition.
Lifestyle Changes
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves circulation and strengthens leg muscles.
- Compression Stockings: These specially designed stockings improve blood flow and reduce symptoms.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on veins.
- Elevating Legs: Elevating your legs above heart level several times a day can ease symptoms.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For more severe cases, interventional radiologists and vascular specialists offer minimally invasive treatments, such as:
- Sclerotherapy: A solution is injected into the vein, causing it to collapse and fade.
- Endovenous Ablation Therapy: Heat or laser energy is used to close off varicose veins.
- Microphlebectomy: Small incisions are made to remove varicose veins.
Surgical Treatments
In rare cases where other treatments are not effective, surgery such as vein stripping may be performed to remove the affected veins.
Preventing Varicose Veins
While it may not always be possible to prevent varicose veins, adopting certain habits can help reduce your risk:
- Stay active and avoid long periods of sitting or standing.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Wear compression stockings if you are at risk.
- Elevate your legs regularly.
- Avoid tight clothing that restricts blood flow.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are more than just a cosmetic concern; they can significantly impact your quality of life. The good news is that advances in medical science offer effective, minimally invasive treatments. If you’re experiencing symptoms, consult a healthcare professional to explore the best treatment options for you.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, you can take proactive steps to manage or prevent varicose veins and maintain healthy circulation.