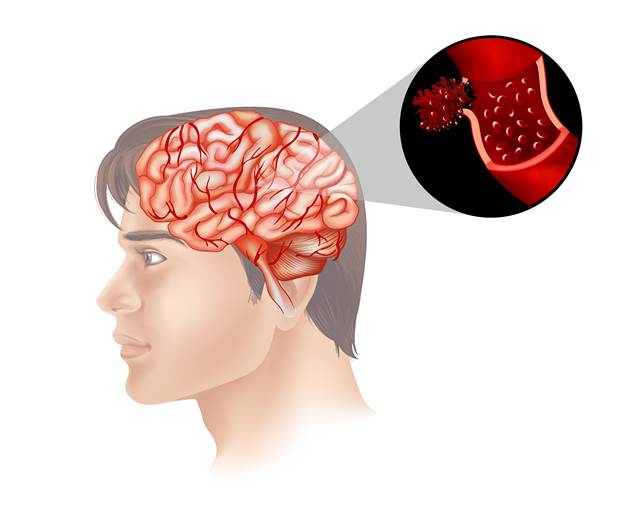
Carotid artery disease happens when fatty deposits clog the carotid arteries situated in the neck. These arteries play a vital role in supplying blood to the brain. When plaque builds up, the risk of strokes increases, posing serious health concerns. Traditionally, carotid endarterectomy has been the go-to treatment for severe cases. However, advancements in medical technology have introduced carotid stenting as a modern alternative. Carotid stenting is a less invasive procedure that removes the blockages and prevents strokes. This article focuses on explaining how carotid stenting prevents strokes and its significance in modern medicine. We’ll uncover crucial insights about this underutilized medical innovation.
Grasping the Basics of Carotid Stenting and Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid arteries are essential components located on each side of your neck. They transport oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the brain. When these arteries develop fatty deposits, known as plaque, it leads to a condition called carotid stenosis. Over time, plaque accumulation narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow to the brain. This can lead to an increased risk of having a stroke.
Understanding the symptoms and risk factors associated with carotid artery disease is crucial. Some common symptoms include sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, or vision problems. Factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, and high cholesterol can elevate the risk.
When dealing with carotid artery disease, carotid stenting advantages become apparent. The procedure involves placing a small metal stent inside the artery to widen it and restore normal blood flow. This approach offers a viable alternative to traditional methods, providing a chance to treat those who might not be good candidates for surgery. Carotid stenting recovery time tends to be quicker, making it increasingly attractive for those seeking efficient solutions.
Key Benefits and Risks of Carotid Stenting
There are numerous carotid stenting advantages worth highlighting. First and foremost, it’s a minimally invasive procedure. This means it requires no large incisions. Instead, a small tube is inserted through a tiny cut in the groin or arm. Patients often enjoy shorter hospital stays, thanks to the quick recovery time. Benefits of carotid stenting also include the improved blood flow and reduced chances of another stroke.
Although the procedure is advantageous, potential risks of carotid stenting do exist, like with any medical procedure. Possible complications can include bleeding, infection, or even a reaction to anesthesia. Nevertheless, the progress in technology and methods has greatly minimized these risks.
One of the primary carotid stenting advantages is its effectiveness in high-risk individuals. People who may struggle with the traditional surgical approach—such as the elderly or those with other health issues—are potential candidates. This procedure helps in preventing strokes by clearing blockages, thus reducing the threat.
Carotid stenting vs endarterectomy often comes up when considering treatments. Endarterectomy is a surgical process that removes plaque directly through a cut in the neck. On the other hand, stenting adds flexibility, with a less invasive approach, while still offering positive outcomes. Technological advancements ensure that both methods maintain a high level of safety and efficacy.
Navigating the Path to Safe Carotid Stenting: From Evaluation to Recovery
Let’s dive into navigating through the process of carotid stenting. It begins with determining who needs carotid stenting. Ideal candidates include individuals with a significant artery blockage or those facing a high risk from traditional surgery. Medical professionals carefully evaluate each case to ensure the best approach. Evaluations usually include imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs, providing detailed views of the arteries.
Before the procedure, doctors discuss potential risks and benefits, setting realistic expectations. On the day of the procedure, expect a straightforward experience. The medical team focuses on safeguarding against any potential strokes during the stenting.
Here’s a basic step-by-step of what happens: 1. Anesthesia is administered to keep you comfortable. 2. A small incision is made in a blood vessel. 3. A tube is inserted and guided to the blockage. 4. A stent is deployed to widen the artery. 5. The path through the artery is reopened, improving blood flow.
After carotid stenting, recovery typically takes just a few days. Most patients are ambulatory quickly, which diminishes the traditional recovery time associated with surgical options. Follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor progress and ensure the stent’s success. Long-term care might include regular check-ups and lifestyle changes to maintain cardiovascular health.
The long-term effects of carotid stenting provide peace of mind. With normal blood flow restored, the risk of future strokes diminishes. The role of doctors and the medical team in ensuring successful outcomes can’t be understated. Expertise and careful attention to each patient’s needs make a significant difference in recovery quality.
In conclusion, understanding the benefits of carotid stenting provides crucial insights into a vital medical breakthrough. Emphasizing less invasive procedures like stenting allows more people to receive adequate treatment and significantly reduces stroke risk. This innovative approach offers new hope to many in need of enhanced care.